 |
| This is a picture of monosaccharides. |
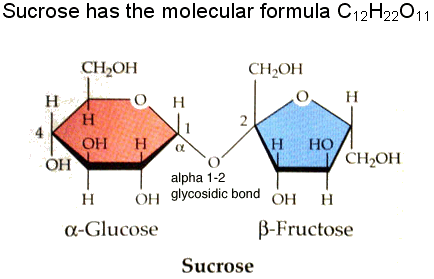 |
| This is a picture of Sucrose which is a disaccharid, and Glucose and Frutose which is a monosaccharide. |
In Biology, we have been studying and learning about biochemistry. I have learned alot of things about macromolecules, like how they are big molecules that are the building blocks of most cells. The four main types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Monomers are composed of sugars, amino acid, fatty acid, and nucleotides. These individual components are linked together, and they are built up of one building block. Monomers are joined together by a process called dehydration synthesis. A chain that is formed when monomers are linked together is a polymer. A polymerase enzyme joins monomers together. Polymers are broken down by a process called hyrolysis, in which a water molecule comes in and breaks a covalent bond between two polymers and the hydroxide ion from the ion and the oxygen bond to either monomer.
In order to build a polysaccharide I arranged the sugar monomers by putting four of them in a row in the build a carbohydrate activity. Building blocks of molecules that are not used to build carbohydrates is the nucleotide, fatty acid and amino acid. Sugar is stored as glycogen in the human body for energy. Starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose. Plants are essential to animal life because animals take advantage of the ability of plants to manufacture sugar and other nutrients. Starch is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. Starch is digested by animals by beginning in the mouth with salivary amylase that continues in the small intestine with pancreatic amylase. Saturated fat is a fat that consists of triglycerides containing only saturated fatty radicals. It is the main dietary cause of high blood cholesterol.
The lab that we did consisted of testing different types of sugars, and classifying them as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. The monosaccharides stays clear when using Iodine solution. Glucose would be an example of a monosaccharide. Mono means one, di means two, and poly means many. We tested different sugars using Benedict's and iodine solutions. To identify a sugar is a disaccharide, by using Benedict's Solution it turns out to be a blue color. Sucrose would be a disaccharide. A polysaccharide has no change in color when using Benedict's solution. When a sugar has a color change in Benedict's solution it is a monosaccharide and it turns a bright orange. Starch is a polysaccharide, and Fructose is a monosaccharide. To identify that a sugar is a monosaccharide, by using iodine solution it turns out to be a clear color. Three elements that are in all carbohydrates are oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon. By doing this lab and studying about the types of different macromolecules, I have a good understanding of how they function and work.
No comments:
Post a Comment